ZalCG: Transonic channel with a circular bump
This example uses ZalCG in Inciter to compute a stationary transconic flow field in a channel with a circular bump on the lower wall.
This is a popular test problem, also known as Ni's test case. The problem consists of a channel with a circular bump in the bottom. The length of the channel is 3 units, its height is 1, and the width is 0.5. We set inlet Mach number to equal 0.675. Since the solution converges to steady state, the most efficient ways to compute this problem are to use implicit time marching or local time stepping [1] of which ZalCG implements the latter allowing taking larger time steps for larger cells.
Problem setup
The mesh, shown below, consists of 59,686 tetrahedra connecting 11,686 points. The initial conditions prescribe the Mach number of 0.675. At the inlet and outlet characteristic farfield boundary conditions are applied, while at the four sides symmetry (free-slip) boundary conditions are set.
 Surface mesh for computing the transconic channel flow with a circular bump, nelem=60K, npoin=12K.
Surface mesh for computing the transconic channel flow with a circular bump, nelem=60K, npoin=12K.Code revision to reproduce
To reproduce the results below, use code revision 1bdbb78 and the control file below.
Control file
-- vim: filetype=lua: print "Bump" ttyi = 1000 cfl = 0.7 solver = "zalcg" stab2 = true stab2coef = 0.05 steady = true residual = 1.0e-9 rescomp = 1 part = "rib" ic = { density = 1.0, pressure = 1.0, -- sound speed: a = sqrt(1.4*1.0/1.0) = 1.1832 -- free stream Mach number: M = 0.675 -- u = M * a = 0.7987 velocity = { 0.7987, 0.0, 0.0 } } mat = { spec_heat_ratio = 1.4 } bc_sym = { sideset = { 3 } } bc_far = { density = ic.density, pressure = ic.pressure, velocity = ic.velocity, sideset = { 4 } } fieldout = { iter = 10000 } diag = { iter = 10, format = "scientific", precision = 12 }
Run on 32 CPUs
./charmrun +p32 Main/inciter -i bump.exo -c bump.q -r 100000
Convergence to steady state
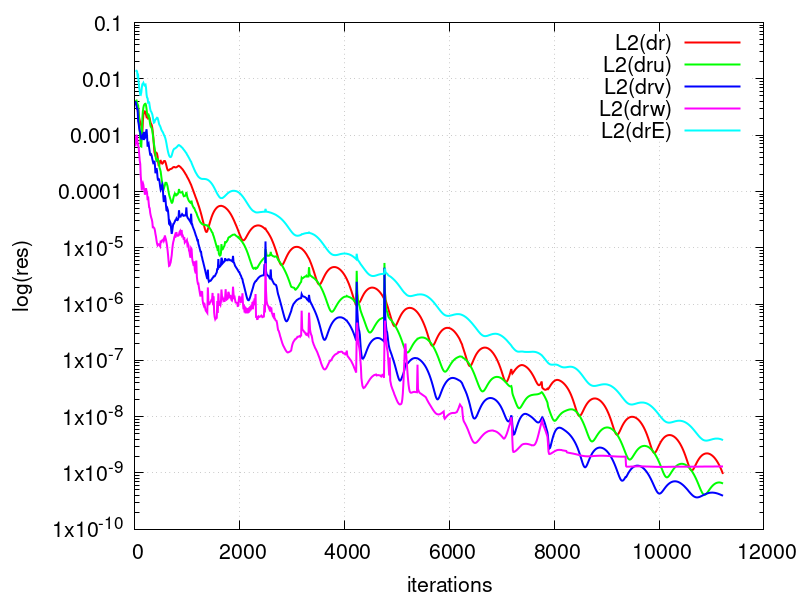
The figure below shows the convergence history of the L2-norms of the residuals of the conserved quantities.
Visualization
ParaView can be used for interactive visualization of the numerically computed 3D fields as
paraview out.e-s.0.32.0The converged Mach number distribution on the channel surface is depicted below.
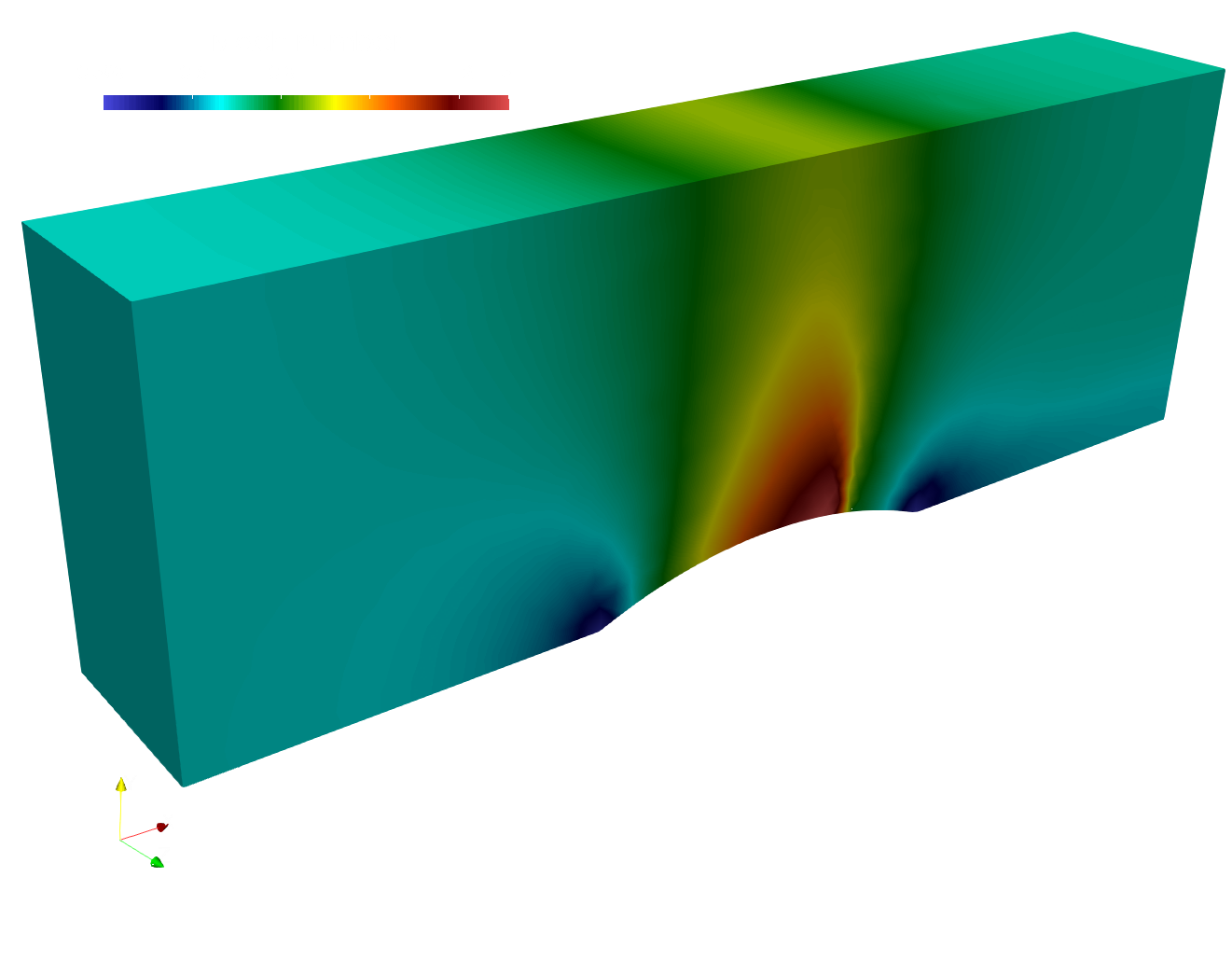 Converged Mach number distribution on the channel surface.
Converged Mach number distribution on the channel surface.References
- R. Lohner, Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Techniques: An Introduction Based on Finite Element Methods, Wiley, 2008.